SPACE
CHALLENGE
Canon Electronics’ Challenge
~The origin story and History~
Origin
The origin story

1999: Sakamaki is appointed President of CE with dreams of entering the space industry. From his experience participating in many new product launches as a member of Canon Inc.'s R&D division, he knew that CE possessed the technology and expertise in precision machines and optics to disrupt the satellite manufacturing market.
2002: Sakamaki is inspired by a conversation with a friend living abroad. An idea, that "the coming age will belong to those who tame near-Earth space," left a deep imprint and Sakamaki felt instinctively, "this is our chance!"
With a clear path to realizing his dream, Sakamaki implemented a series of bold reorganizations in management in order to build up the necessary funds and worked tirelessly to recruit talent and experience. In 2009, Sakamaki declared Canon Electronics' entry into the space industry and officially kicked off CE's challenge.
History
Major milestones in CE Space
- 2017.06
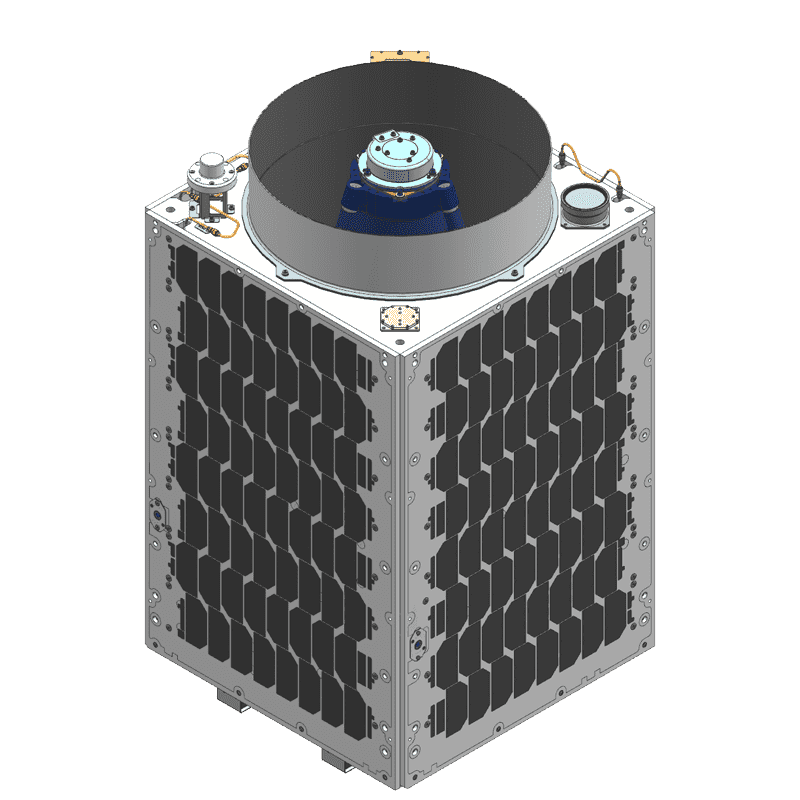
- Launch of the prototype micro satellite CE-SAT-I from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in India onboard PSLV-C38. The satellite entered a 500km sun-synchronous orbit. This marks the first successful launch of a self-funded satellite by a private company in Japan's history.
- 2017.08
- Canon Electronics, in partnership with IHI Aerospace, Shimizu corporation, and Development Bank of Japan, establishes the "New Generation Small Rocket Development Planning Co. Ltd."
- 2018.02
- Successful launch of the 10 m JAXA sounding rocket SS-520-5. Canon Electronics provided several components including avionics.
- 2018.07
- Canon Electronics, in partnership with IHI Aerospace, Shimizu Corporation, and Development Bank of Japan, establishes Space One Co., Ltd. to operate as a commercial space transport service business for small satellites.
- 2020.10
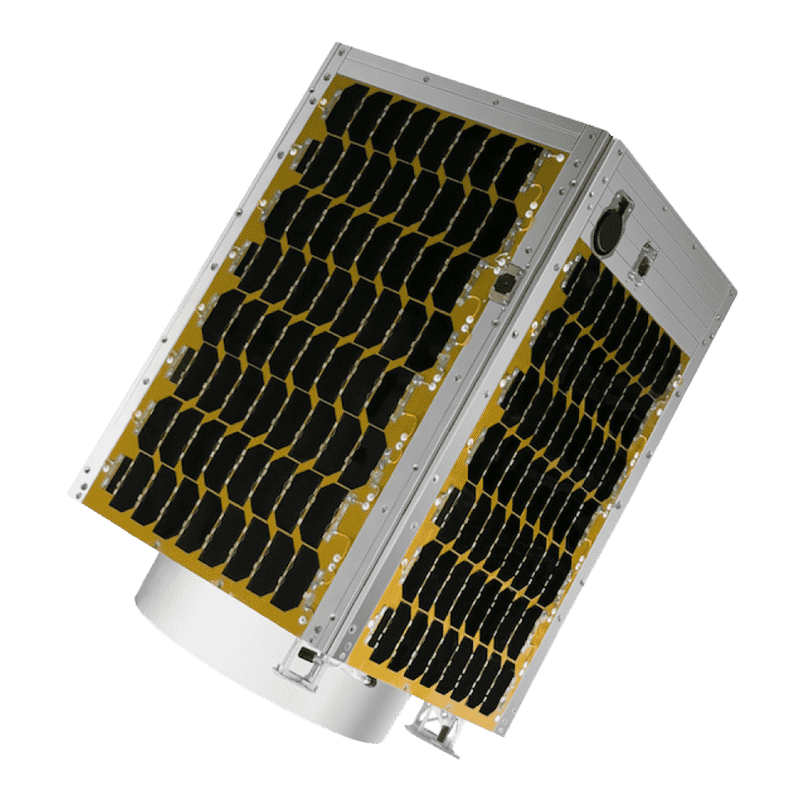
- Launch of third microsatellite CE-SAT-IIB from New Zealand. The satellite entered a 500km sun-synchronous orbit. Equipped with three cameras including super high sensitivity camera, along with other in-house developed components. The satellite will go through a 2 year demonstration experiment for forthcoming production of cassegrain reflectors as series.
BUSINESS
Three Pillars of Satellite Business
SATELLITE
Ready-made and Semi-custom Satellites
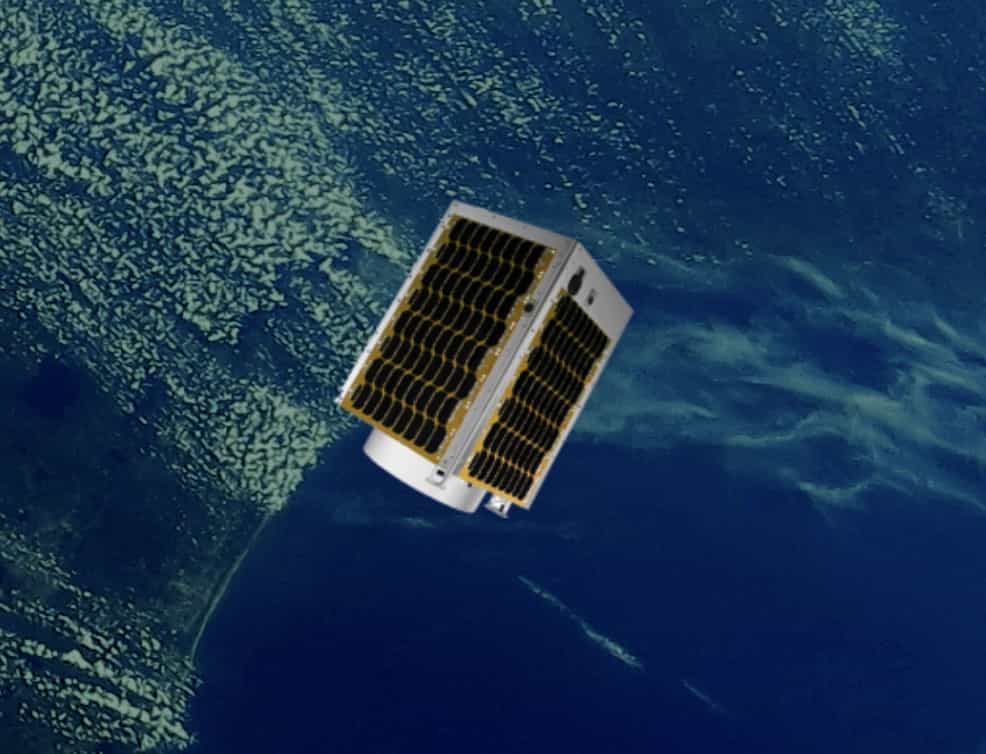
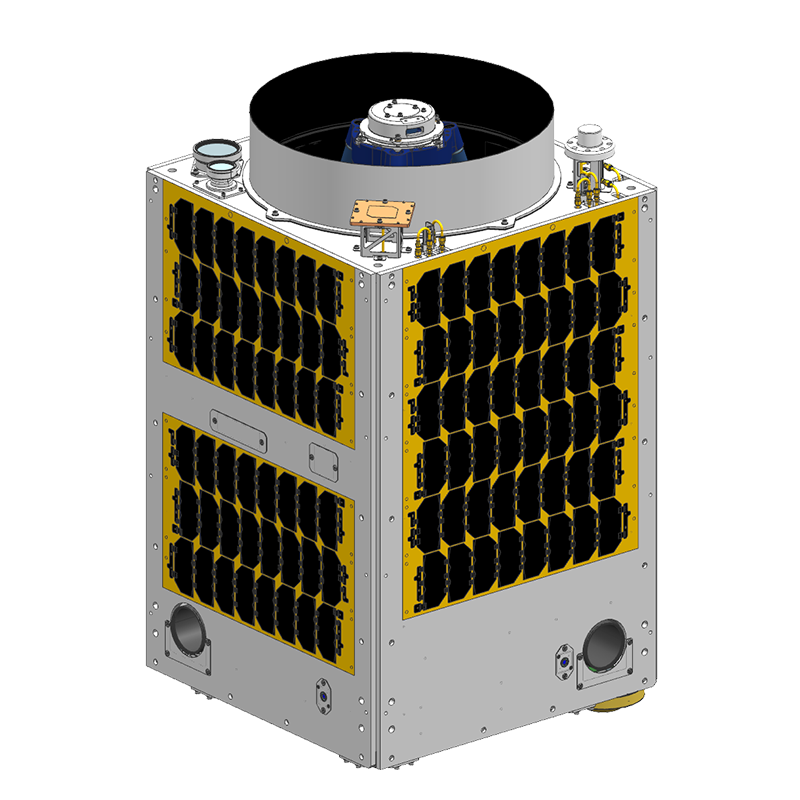
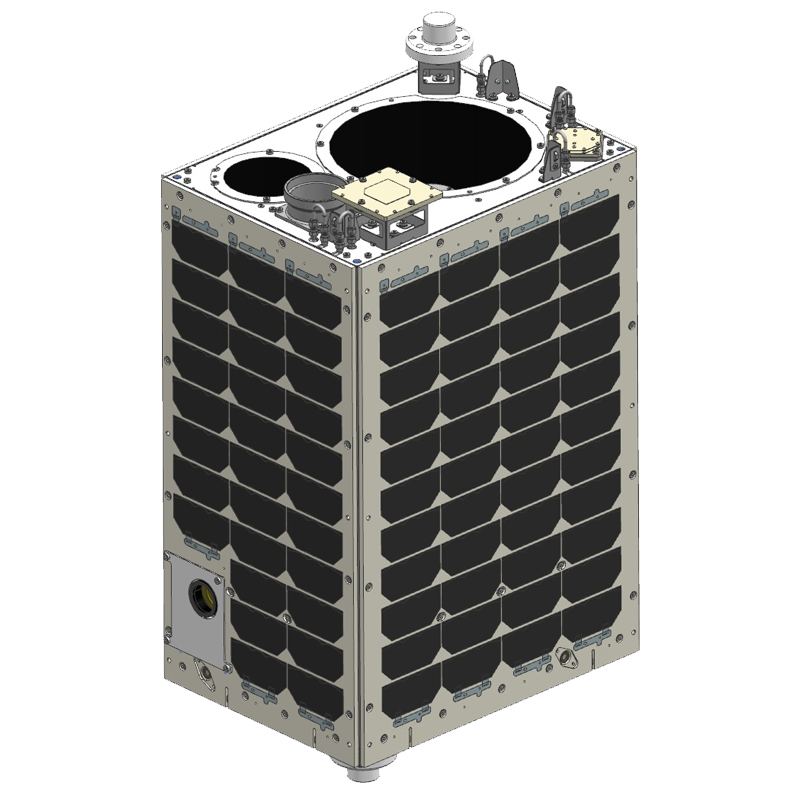
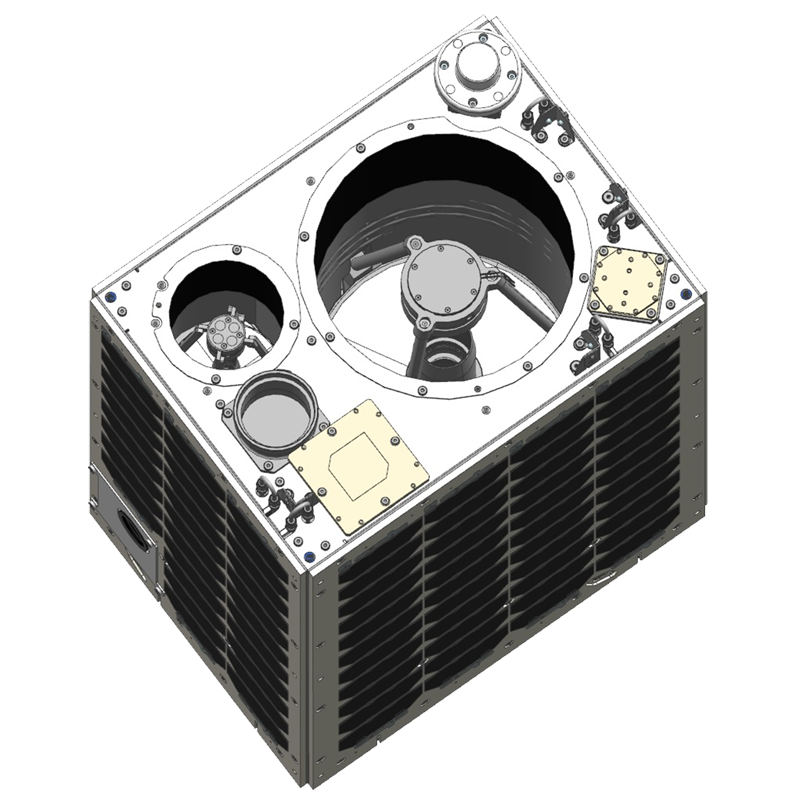
Canon Electronics can meet users' various needs with its micro satellite platform. Leveraging the Canon group's expertise in optics, the optical payloads are capable of world-class resolution imagery and video. A range of satellites with differing diameter optics are currently under development, further enhancing CE's ability to tailor the satellite to customer needs at low cost and fast lead times. CE looks forward to providing industry, academic institutions, startups, and other interested parties with reliable and affordable space platforms to further human use of space and improve quality of life.
Micro-satellite CE-SAT-IE
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
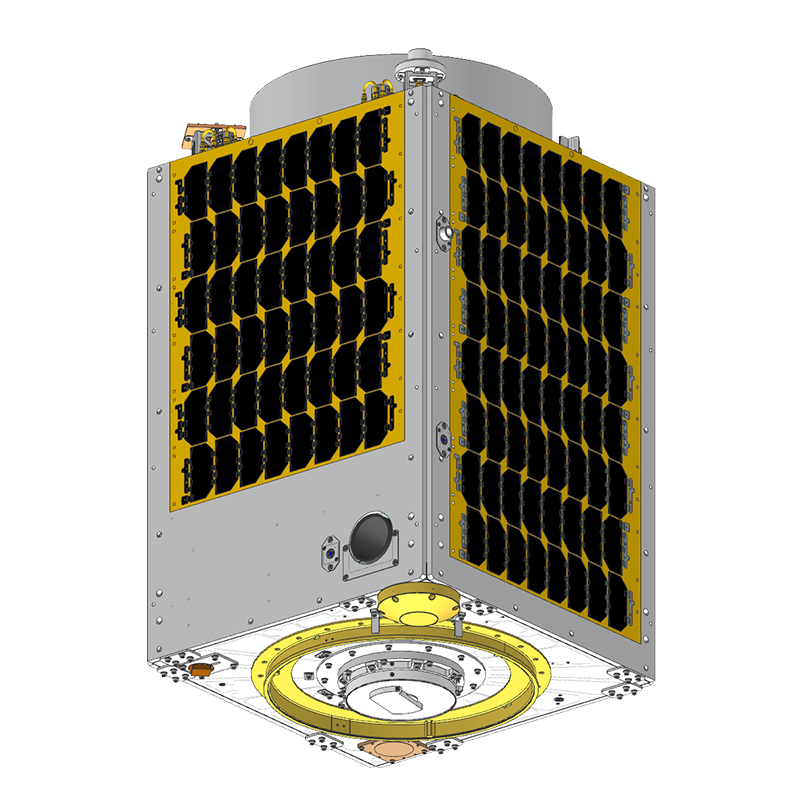
Microsatellite CE-SAT-IIB
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
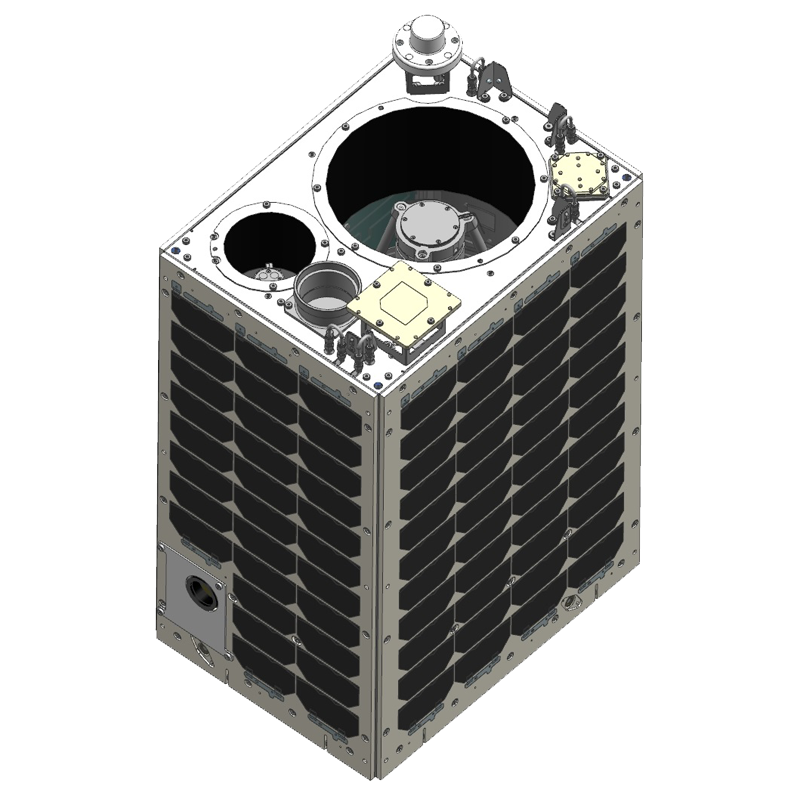
Prototype Micro Satellite CE-SAT-I
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
COMPONENTS
② In-house Components
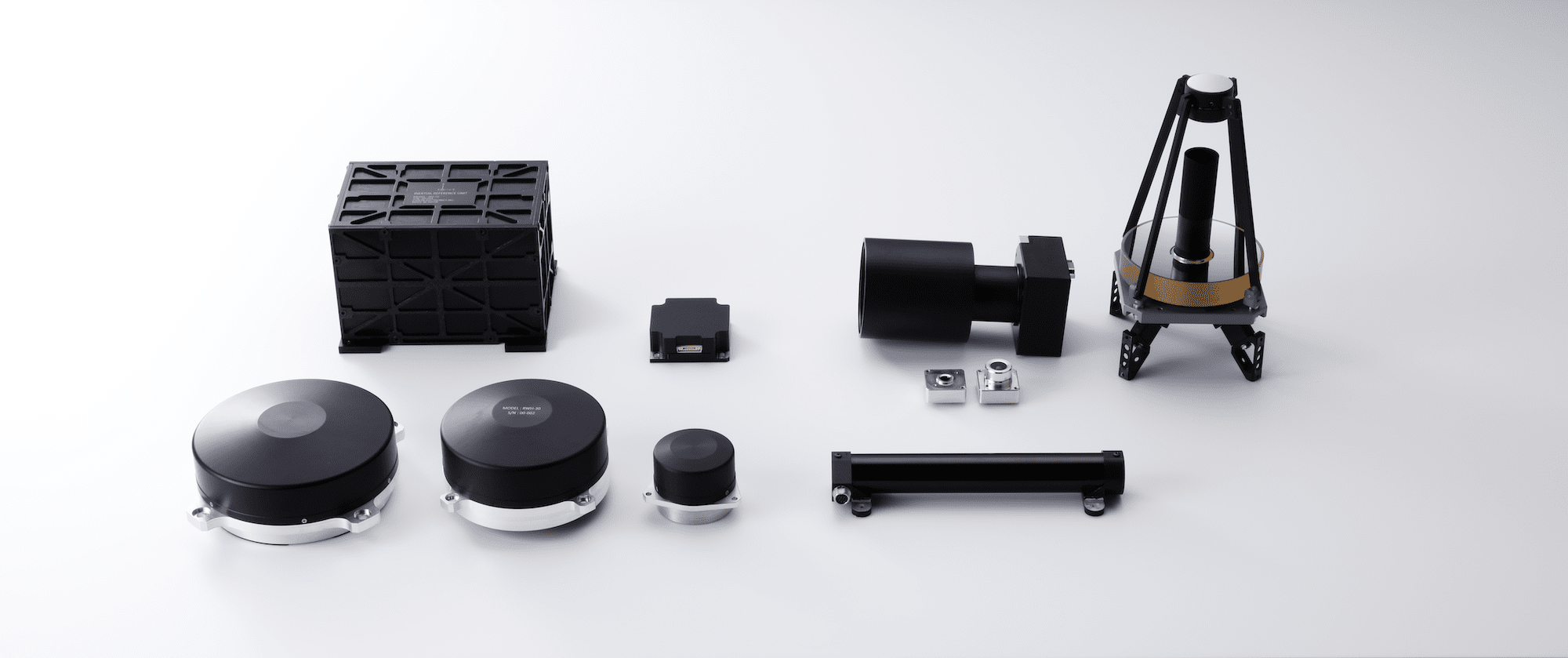

- Optical payloads
-
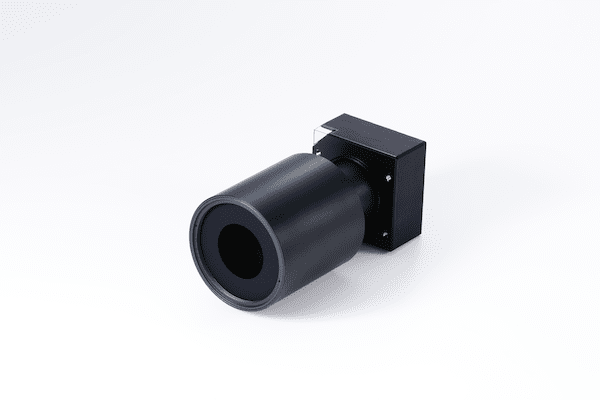
Telescopes and cameras leveraging the full optical expertise of Canon
Space Telescopes


Optical system for high-resolution Earth observation satellites
- Actuators
-
Satellite actuators based on CE experience with motors and magnetic components
Magnetorquer
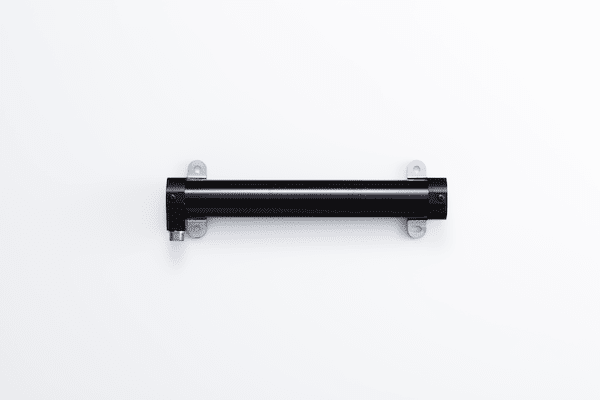

Magnetic actuator for controlling spacecraft attitude via interactions with the Earth magnetic field
Reaction Wheel
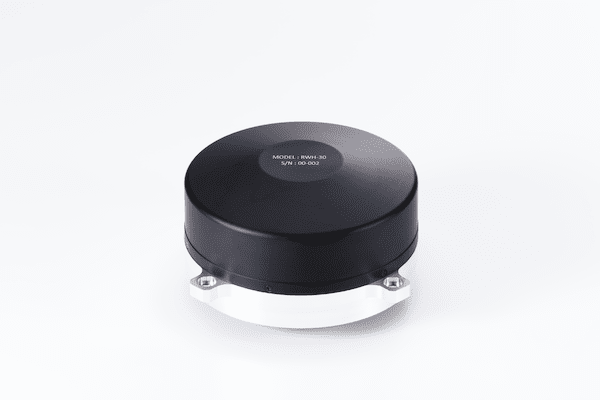


Actuator for controlling spacecraft attitude via momentum transfer to a rotating wheel (mass)
- Sensors
-
Precise sensors for determining satellite attitude
Sun Sensor
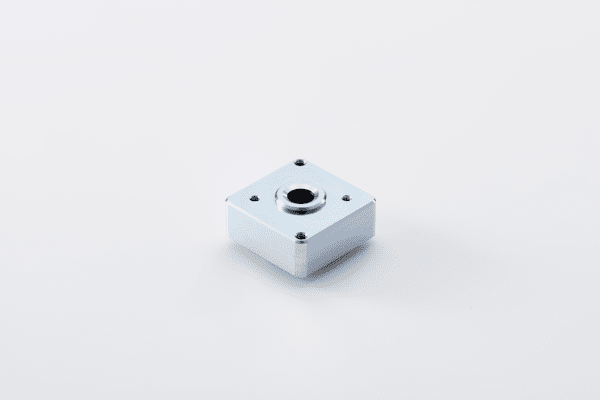

Determines the body-frame direction of the sun by detecting sunlight
Star Tracker


Calculates the spacecraft attitude using positions of known celestial objects
Geomagnetic Sensor
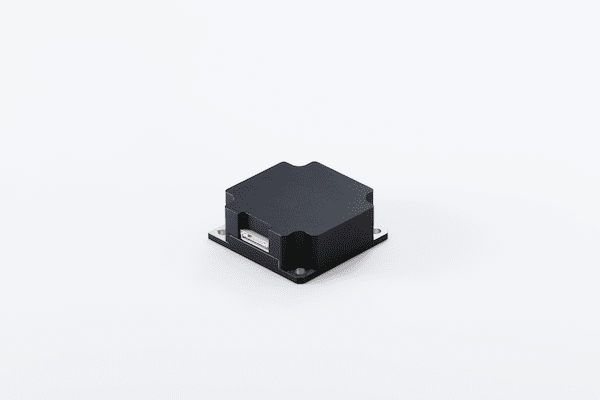

Measures the geomagnetic field vector by detecting differences in the coil current
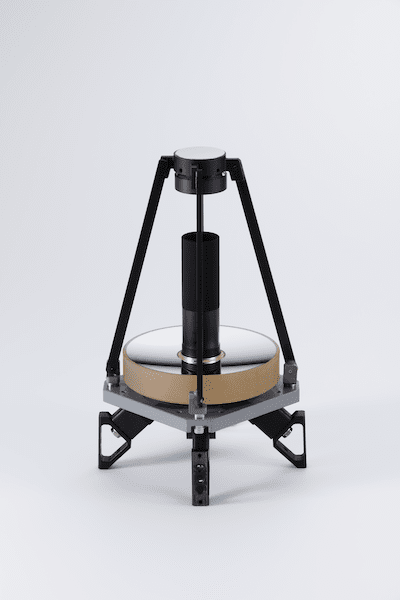
Inertial Reference Unit


Measures angle and angular rate; comprised of multiple gyroscopes
DATA
Satellite Imagery, Video, and Analytics

Canon Electronics' micro satellite leverages the Canon group's expertise in optics to allow high resolution photography and videography across the globe. High resolution images contain valuable data, with applications ranging from agriculture, geology, to market research. CE, in addition to providing detailed and often beautiful images, is also working to automate the extraction of valuable data. From event photos from 500km to scientific and business observations, CE is ready to support your satellite data needs.
Examples of Satellite Data Use
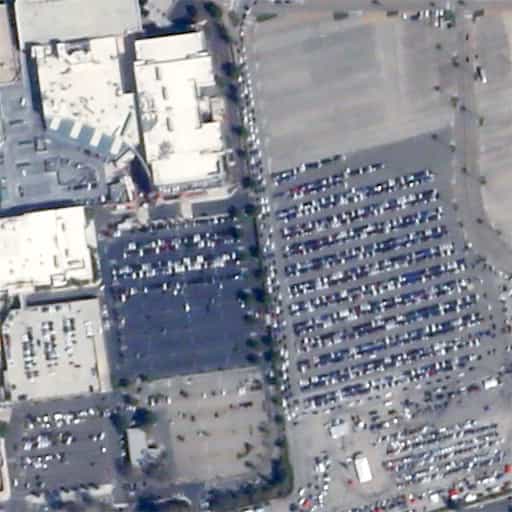
Monitoring parking lots

|
||

|
With photographs at regular intervals, the use rate of parking lots may be calculated. Tracking changes in use with seasons or time of day allows improvements in logistics and resource allocation. |
|
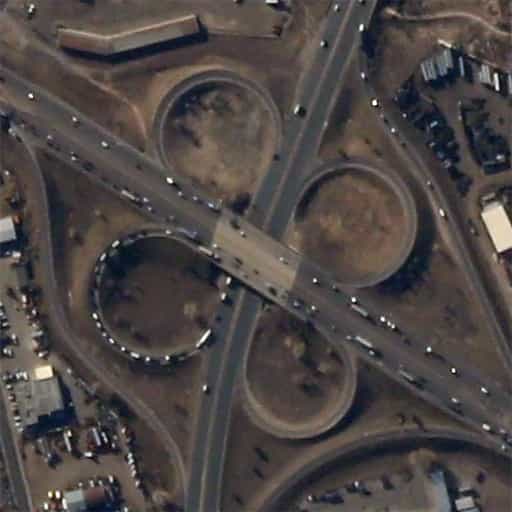
Monitoring traffic conditions

|
||

|
By monitoring traffic density or lengths of traffic jams, it is possible to determine fastest routes in near real time. CE-SAT-I imagery allows distinction between semi-trailer trucks and passenger vehicles, which further aids in optimizing navigation routes. |
|
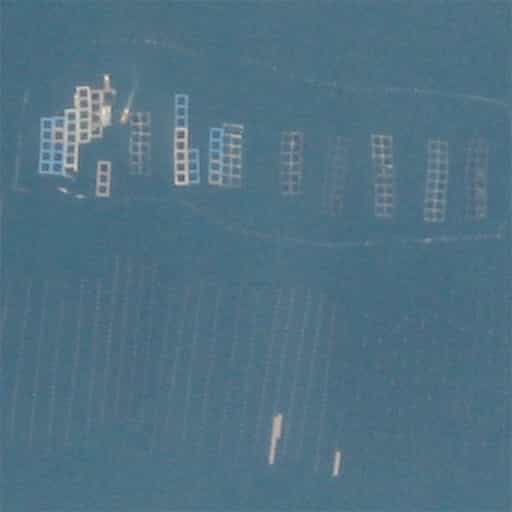
Fishing industry

|
||

|
High resolution satellite imagery can gather data from remote locations, including over water. This allows monitoring of fish hatcheries or vessels moored off-shore. |
|
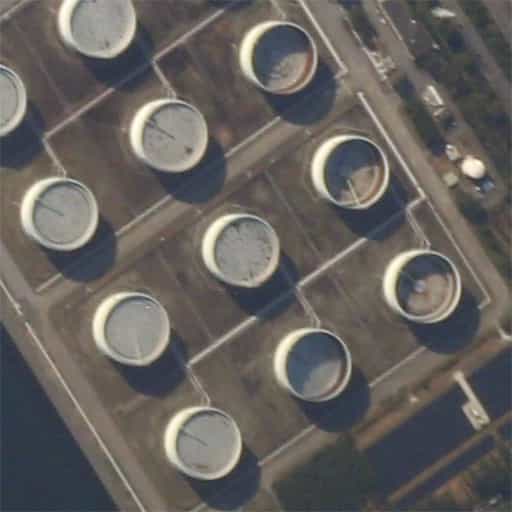
Oil industry

|
||

|
External floating roof tanks are used around the world for storing petroleum products. With high-resolution satellite imagery, it is possible to measure the contents of the tanks, giving market analysts an edge. |
|
SATELLITE
PHOTO GALLERY
-
Ultra High Sensitivity Camera
-

Ultra High Sensitivity CameraTokyo (Mozaic image) -

Ultra High Sensitivity CameraAround Tokyo station -

Ultra High Sensitivity CameraArakawa and TOKYO SKYTREE -

Ultra High Sensitivity CameraParis -

Ultra High Sensitivity CameraLondon -

Ultra High Sensitivity CameraNoth Pole, Alaska -

Ultra High Sensitivity CameraDubai Expo (Day) -

Ultra High Sensitivity CameraDubai Expo (Night) -

Ultra High Sensitivity CameraSuper moon 2021 -
Ultra High Sensitivity CameraInternational Space Station -

Ultra High Sensitivity CameraInternational Space Station ( Clipped image )
-
EOS 5D Mark Ⅲ
-

EOS 5D Mark ⅢThe Moon and Mars -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢComet NEOWISE (C/2020 F3) -
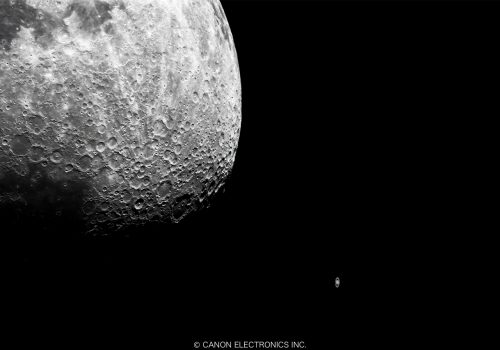
EOS 5D Mark ⅢThe Moon and Saturn -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢSydney -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢLos Angeles -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢAlaska -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢShopping mall (Los Angeles) -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢPhoenix Sky Harbor International Airport -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢTokyo (Shinagawa) -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢVenice -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢDubai -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢCairo (Giza pyramid complex) -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢCanon Electronics Akagi Plant -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢMt. Fuji (Yoshida Trail) -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢMt. Everest -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢTokyo (Shinjuku) -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢSiem Reap (Angkor Wat) -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢAntarctica -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢAthens (Parthenon) -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢNagoya (stitched) -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢOsaka -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢGrand Canyon -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢNew York City -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢParis -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢFukuoka -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢUniversal Studios Japan -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢBlack Rock City (Burning Man site) -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢBahamas (Paradise Island) -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢMoon -

EOS 5D Mark ⅢSan Jose
-
PowerShot S110
-

PowerShot S110Tunisia -

PowerShot S110Lake Titicaca -

PowerShot S110Florida -

PowerShot S110Honshu -

PowerShot S110Italy and Greece -

PowerShot S110Turkey -

PowerShot S110California (Thomas Fire) -

PowerShot S110Maldives -

PowerShot S110Egypt -

PowerShot S110Lake Baikal -

PowerShot S110Aurora Australis -

PowerShot S110Grand Canyon -

PowerShot S110Himalayas -

PowerShot S110Dawn -

PowerShot S110Orion -
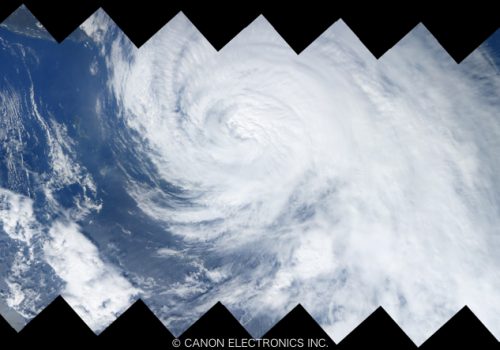
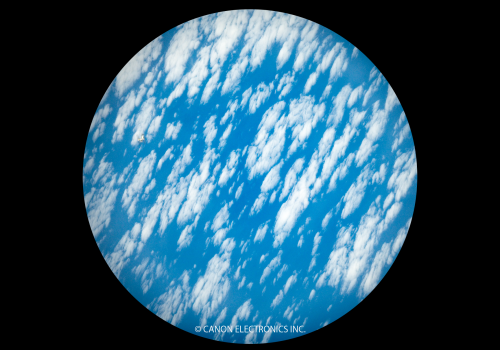
PowerShot S110Typhoon Talim (stitched) -

PowerShot S110Earth and Moon -

PowerShot S110Honshu (stitched)